Grammar and literacy glossary: R to S
Need a refresher on fronted adverbials or the passive voice? Get to know what your child is learning at school with our guide to common terms and phrases used in schools.
For help with general educational terms, take a look at the Education glossary.
For help with maths terms, take a look at the Maths glossary.
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
Relative clause
A relative clause is a type of subordinate clause. It is connected to the main clause by a relative pronoun such as ‘that’, ‘which’, ‘who’, ‘whom’ or ‘whose’.
I enjoyed the film that we saw last night.
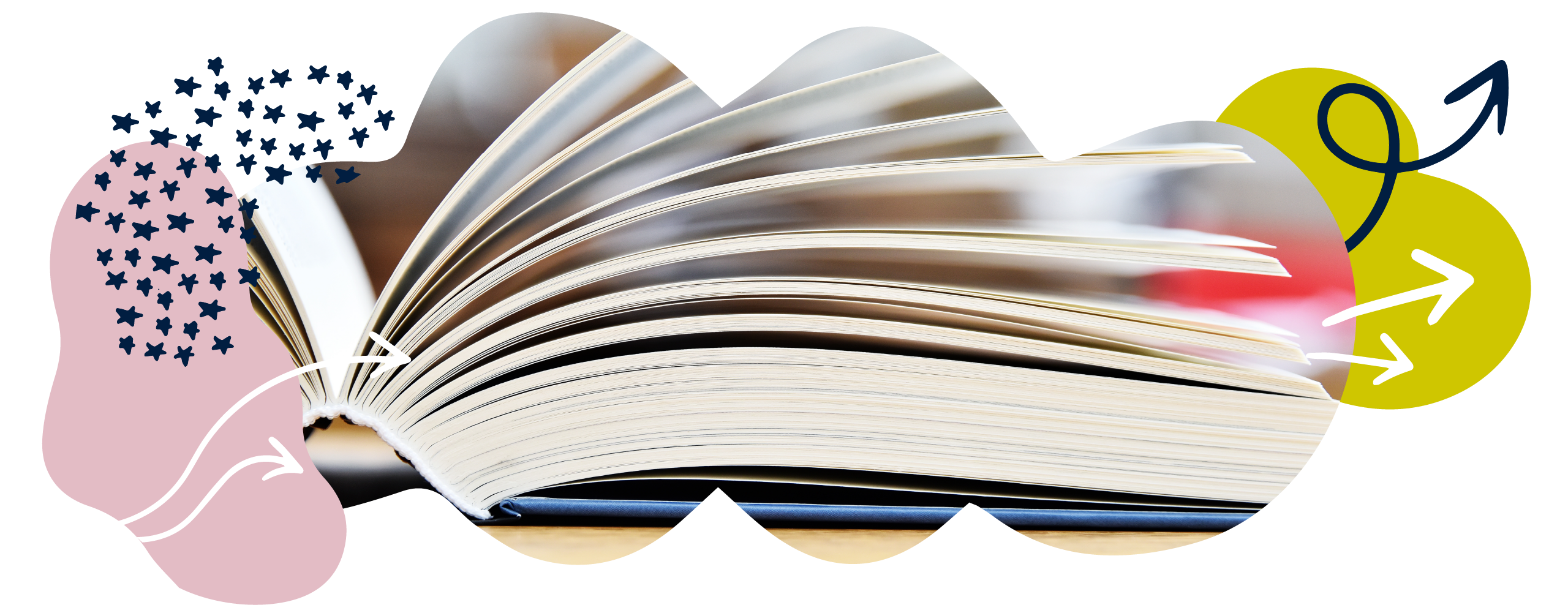
Activity: Suffixes
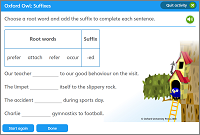
Write a root word and add the suffix to complete each sentence.
Segmenting
To write or spell a word by listening for the sounds in the word and deciding which letters represent those sounds. We say you blend to read and segment to spell.
Semicolon ;
A semicolon can be used between two related main clauses.
The film was brilliant; I had a great time.
A semicolon can separate longer phrases in a list that has been introduced by a colon, or which is more complicated than a simple list of words.
The children need to bring with them: a hot-water bottle or an extra blanket if the weather is cold; a cup, a plate and a bowl; a knife, a fork and a spoon.
Do not use a comma to join sentences or main clauses. If you want to join sentences using punctuation, choose a semicolon, a colon or, if you are writing informally, a dash.
Sentence
A sentence tells you something, asks you something, asks you to do something or exclaims about something. In writing, all sentences start with a capital letter and end with a full stop, question mark or exclamation mark. Sentences consist of one or more clauses. All sentences have a verb and, in most sentences, the verb has a subject.
Single-clause sentence: A single-clause sentence consists of one main clause.
The bird ate the apple.
Multi-clause sentence: A multi-clause sentence consists of more than one clause.
The bird felt hungry and it ate the apple. (Two main clauses.)
Although it had already eaten, the bird ate another apple. (A subordinate clause followed by a main clause.)
Video: What are sentences?
Learn how and when to use different sentence types, including statements, questions and commands.
Video: Sentence types
Help your child learn about sentence types through these grammar activities and fun grammar games.
Sight words
Words you need to learn by sight because they cannot be easily sounded out. (Also see tricky words).
Sound talk
To say the individual sounds that make up a word. (Also see Fred Talk.)
Sounding out
To say the individual sounds that make up a word (sometimes also called Fred Talk or Robot Talk).
Subjunctive
Subjunctive forms can be used in formal language to show that something must or should happen. They can also show that something is unlikely or uncertain.
If I were able to take up a position with you, I would be diligent and punctual.
I note your requirement that applicants be experienced.
Video: What is the subjunctive?
Learn how and when to use the subjunctive form.
Subordinate clause
A subordinate clause helps to give more meaning to the main clause. It cannot exist on its own as it is not a complete sentence. A subordinate clause often starts with a subordinating conjunction such as ‘although’, ‘because’, ‘before’, ‘if’, ‘since’, or ‘when’.
The bird pecked the apple before it flew away.
Video: What is a subordinate clause?
Learn the difference between a clause, a subordinate clause, and a relative clause.
Suffix
A morpheme that can be added to the end of a root word. Different suffixes have different meanings so, when you add a suffix to a word, you change its meaning and make a new word.
fast + er = faster.
sad + ness = sadness.
joy + ful = joyful.
hope + less = hopeless.
apple + s = apples.
advert + ise = advertise.
Activity: Suffixes
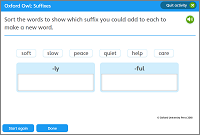
Sort the words to show which suffix you could add to each word.
Video: What are prefixes and suffixes?
Learn how to use prefixes and suffixes.
Syllable
A word or part of a word that contains one vowel sound when you say it.
Vow-el; con-nec-tive.
A syllable sounds like a beat in the word: ‘Vow-el’ has two syllables; ‘Con-nec-tive’ has three syllables.
Synonym
Words that mean the same – or nearly the same – as each other, such as ‘big’ and ‘huge’, or ‘horrible’ and ‘nasty’. The opposite of a synonym is an antonym.
They lived in a big house. They lived in an enormous house.
Activity: Spotting synonyms
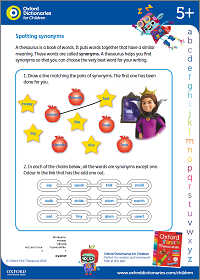
Match the words to their synonyms, and find the odd one out.
Video: What are synonyms and antonyms?
Learn how to use synonyms and antonyms.
Synthesising sounds
Blending or merging the sounds in a word together in speech so you can read the word.
Synthetic phonics
Synthetic phonics is a way of teaching reading. Children are taught to read letters or groups of letters by saying the sound(s) they represent – so, they are taught that the letter ‘m’ sounds like ‘mmmm’ when we say it. Children can then start to read words by blending (synthesising) the sounds together to make a word. Read more about phonics.
